Appearance
Technical Requirements
This guide describes the high-level technical requirements for integration with EarthCODE. Specific configurations and more detailed requirements will be provided during onboarding.
🛠️ Page Under Development
Content is being actively developed and updated for this page. EarthCODE's documentation is a living document and will be continuously updated with detailed reviews.
To ensure accessibility and maximize impact, EarthCODE seeks to integrate mature platforms and services with minimal initial complexity.
EarthCODE Platforms must provide the capabilities for:
- Enabling GitHub-based authentication for Single Sign-On (SSO) and easy discovery of platforms via the EarthCODE Portal.
- Allowing authenticated scientists to develop and execute experiments on platforms, utilizing allocated resources provided through the ESA Network of Resources (NoR).
- Publishing experiment and product metadata as standardized OGC API Records or STAC items to a dedicated GitHub repository. This publishing step enables discoverability and fosters collaboration. (Specifically for FAIR Open Science Platforms)
- Storing final research outputs persistently on the ESA Product Results Repository (PRR) on cloud-optimized formats where possible. (Specifically for FAIR Open Science Platforms)
- Exposing service capabilities (via RESTful APIs or standard interfaces) to support federation and automated execution of workflows. (Specifically for FAIR Infrastructure Platforms)
The Open Science Catalog team will support platforms in defining and validating standard metadata formats, while the EarthCODE Community Platforms will offer guidance, support, and onboarding resources.
Users access platform services through the ESA Network of Resources (NoR), which means platforms must support and maintain the experiments users run, in line with the terms of their NoR contract. Once research is complete, EarthCODE ensures the long-term storage of the resulting data and workflows through the ESA Product Results Repository (PRR) and the Open Science Catalog.
Platforms are expected to continue to be managed and operated by the platform providers, but they will provide the above capabiltiies through standard EarthCODE interfaces, standards and endpoints.
High-Level Breakdown of Work
This section outlines the key functional areas (epics) for integration. These are aligned with EarthCODE’s architecture and roadmap, and each epic corresponds to specific responsibilities and interface requirements.
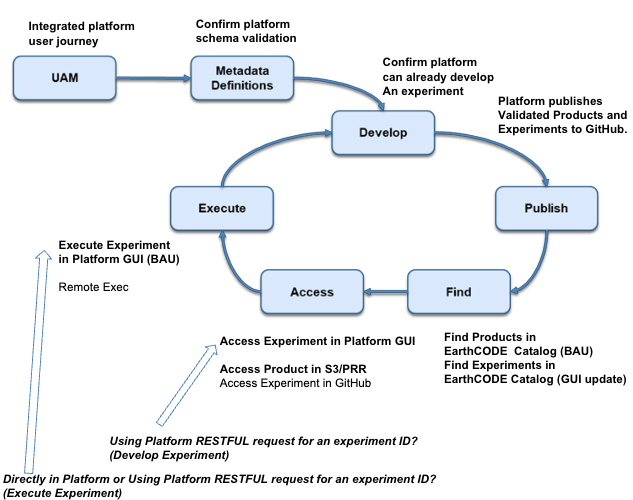
| Epic | Description | Platform Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| User Access Management | Enable Single Sign-On via the EarthCODE Portal to access all integrated services. | Implement SSO with EarthCODE identity. |
| Metadata Definitions | Ensure compatibility with EarthCODE metadata standards, including STAC and OGC API Records. | Confirm EarthCODE schema usage and expose experiment/product metadata in valid format. |
| Develop | Reuse existing tools/platforms to create scientific experiments and workflows. | Support development of experiments with minimal changes, ensuring interoperability. |
| Publish | Push validated metadata and links to products and experiments into the EarthCODE Open Science Catalog. | Automate publishing of metadata to GitHub for ingestion. |
| Find | Make experiments and products discoverable via the Open Science Catalog. | Ensure catalog metadata is rich, accurate, and properly linked. |
| Access | Enable users to retrieve and review experiments, workflows, and product data. | Host data in persistent storage and provide public URLs; support access via catalog. |
| Execute | Allow experiments to be re-executed using original inputs and configurations on the same platform. | Support reproducible execution of published workflows on platform. |
The specific interfaces needed to implement these steps—including Single Sign-On, validation, publishing, and execution—are further defined in EarthCODE's internal technical documentation which will be provided in the tendering documents
FAIR Open Science Platforms Detailed Requirements
FAIR Open Science Platforms within EarthCODE provide comprehensive tooling and environments that support researchers in managing the full lifecycle of scientific workflows in accordance with FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles. These include capabilities for:
- Management of users within projects, groups, and communities
- Discovering, accessing, and reusing scientific datasets and code.
- Tools for developing scientific workflows, which could include GUIs for development and editing tools for workflows - producing experiments and data.
- Automated build, test and deployment (as container images) pipelines and source code management
- Validation of workflow syntax and semantics before execution and workflow compatibility checks against FAIR infrastructure
- Input data and configuration validation for reproducibility
- Monitoring, logging, and observability of development processes
- Providing tools to explore and visualize results data
- Integrating with the ESA Project Results Repository (PRR) for long-term data storage
- Publishing products (described in STAC) and workflows (described in OGC API Records) to the EarthCODE Open Science Catalog.
- Integrating with EarthCODE's Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Providing documentation about the integration and usage of their platform
- Operational guides and service-level agreement definitions
FAIR Infrastructure Platforms Requirements
EarthCODE aims to integrate scalable, cloud-based infrastructure platforms that support the execution of scientific workflows in line with FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles. These infrastructure platforms must ensure reliable, reproducible, and performant workflow execution, while maintaining strong alignment with EarthCODE’s metadata and publication standards.
FAIR Infrastructure Platforms are expected to:
- Implement EarthCODE Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Support using existing STAC definitions for products
- Support using existing OGC API Records for experiments/workflows
- Provide scalable infrastructure for executing workflows at scale, including support for AI/ML models, data cubes, and large time-series datasets, preferably in cloud-optimized formats (e.g., COG, Zarr, NetCDF).
- Offer both human and machine interfaces (RESTful APIs) for data discovery, access, and execution. This includes the ability to:
- Find input datasets through a catalogue UI and/or API
- Access input data through a human interface and machine API (e.g., S3-compatible)
- Execute workflows using references to experiments and workflows defined in the Open Science Catalog. This can be through Support standards such as OGC API - Processes, OpenEO graphs or others, platforms must define which workflow types and data types are supported for reproducibility
- Report status and access execution results
- Allow users to execute experiments published in the catalog using a unique identifier and STAC-based input metadata.
- Provide or support archiving of datasets using the ESA PRR.
- Expose platform functionality as service-based APIs that can be used by the EarthCODE Portal and other platforms for federation, reproducibility, and usability.
- Provide full technical documentation of the services and integration components
- Maintain services with up-to-date versions and ensure operational support
- Integrate into the ESA Network of Resources (NoR) if not already onboarded. Please see https://esastar-publication.sso.esa.int/nonEsaTenderActions/details/2037 for more details and to make an application
- Provide observability of workflow execution processes and manage logging
- Provide Platform SLA
High-Level Architecture and Concepts For Integration
The concepts below summarize the Deep Dive and add technical details
You are highly encouraged to read through the full Deep Dive into EarthCODE Page
Integration between EarthCODE’s FAIR Open Science and Infrastructure platforms depends on well‑defined metadata for both workflows and the data they use. By standardizing these definitions, we enable the following architecture:
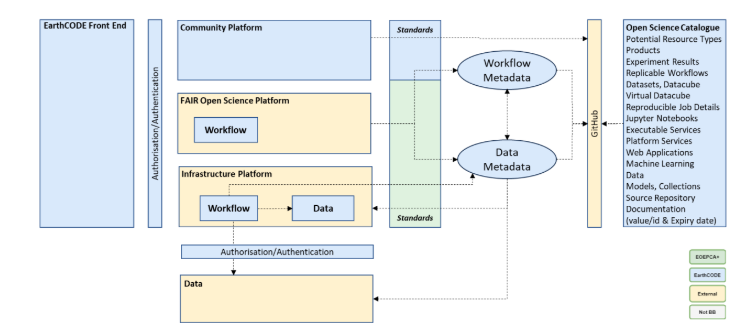
FAIR Open Science Platforms are responsible for creating workflow definitions. Each workflow definition is dependent upon data definitions that describe the input data it consumes and the data (products) it produces as well as configurations to be passed as an environment for the workflow. All of this should be generated automatically by the platforms to make it easy for the users to publish to the Open Science Catalog.
Infrastructure Platforms ingest workflow definitions and execute them close to the required input data. Access to data used by a workflow is typically provided on the same platform, reducing transfer overhead and the risk of failure. In some cases, data hosted on Infrastructure Platforms can be shared back to FAIR Open Science Platforms—for example, to support a local Python script with test data before conversion into a full workflow.
Input metadata describes the input data for a workflow and guides both execution and user interfaces. FAIR Open Science Platforms and Infrastructure Platforms may specialise in one or more types of workflows and in one or more types of Data. Consistent metadata definitions also facilitate the creation of GUIs and tools to help execute and manage workflows. Once validated, workflow definitions, data definitions and related artifacts can be published to the Open Science Catalogue and exploited by the Community Platform.