Appearance
Integrating New platforms to EarthCODE
🛠️ Page Under Development
Content is being actively developed and updated for this page. EarthCODE's documentation is a living document and will be continuously updated with detailed reviews.
This guide walks you through the process of integrating your platform into the EarthCODE ecosystem. It's designed specifically for platform providers interested in connecting their Earth Observation tools, computational resources, and data services to EarthCODE, enabling researchers to collaboratively develop, execute, and share FAIR-compliant Earth science research. This page provides an overview, the Technical Requirements provide detailed requirements for integration and the How to Apply Page gives you details on how to apply to become a platform provider to EarthCODE.
You are highly encouraged to read through the Getting Started Pages, especially the Deep Dive into EarthCODE Page for getting an idea about the overall context and concepts of EarthCODE before going through these pages.
The Integration Strategy
EarthCODE is built as an open, extensible, modular ecosystem designed to grow. Integrating new platforms into EarthCODE means connecting existing Earth Observation (EO) tools, data services, and research environments to a shared, federated infrastructure that supports FAIR and Open Science by design. These platforms help researchers conduct science collaboratively, develop reproducible workflows, and share their results through the EarthCODE Open Science Catalog.
Generally, EarthCODE's strategy for new platforms is to:
- The goal of integration is to expand the capabilities of EarthCODE by including operational EO platforms that bring with them their own user communities and existing research outputs (data products, workflows, experiments).
- Expand EarthCODE using existing EO platforms that offer data access, processing, and storage services in a federated manner. The platform providers are expected to continue maintaining and managing their platforms.
- Integrate and reuse components that scientists already use, such as platforms, EOEPCA+ building blocks and open-source components via integration rather than development of all together new tools.
- Establish a sustainable framework for managing scientific research outputs according to FAIR principles.
- Ensure that experiments developed on integrated platforms can be reproduced using the same workflows, inputs, and configurations
- Provide persistant storage for research results in an integrated manner
- Strengthen and expand the Earth Observation science community by supporting collaboration, openness, and reuse of research and by including open-source tooling and platform communities.
From the perspective of the user, the platforms provide a place to develop reproducible workflows (potentially across several platforms), accessing data, and publishing items to the catalog. Platforms will offer both or either (1) FAIR Open Science Platforms for discovering and reusing data and publishing to the catalog and developing algorithms (workflows) and (2) FAIR Infrastructure and computing resources for running workflows and for serving data.

Please refer to the Technical Requirements Page for technical details of integrating with EarthCODE.
FAIR Open Science Platforms
note to self maybe rename this to something more intuitive like FAIR dev platforms/tools?
FAIR Open Science Platforms within EarthCODE provide researchers with tools and environments to perform scientific research in line with FAIR (Findable, Accessible,Interoperable, and Reusable) and Open Science principles. These platforms support the complete research lifecycle—from initial data discovery, visualization and data exploration, reuse of existing datasets and code, through to workflow development and publication of resulting workflows and data to the ESA PRR and the Open Science Catalog.
Researchers have the choice to develop/run their scientific workflows entirely within EarthCODE’s integrated FAIR Infrastructure Platforms or use their own local, institutional computing resources instead. Regardless of the computing environment, these platforms ensure researchers adhere to FAIR guidelines, enable them to develop and manage workflows, and publish FAIR items to EarthCODE.
Their key responsibilities are:
- Discovering, accessing, and reusing scientific datasets and code.
- Developing scientific workflows and producing experiments and data.
- Automated build, test and deployment (as container images) pipelines and source code management
- Providing tools to explore and visualize results data
- Integrating with the ESA Project Results Repository (PRR) for long-term data storage
- Publishing datasets, code, and results to the EarthCODE Open Science Catalog.
- Integrating with EarthCODE's Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Providing documentation about the integration and usage of their platform
FAIR Infrastructure Platforms
FAIR Infrastructure Platforms integrate scalable computational resources required to execute scientific workflows developed by researchers using FAIR Open Science Platforms or other tools (through standard protocols). These platforms offer robust cloud-based services, providing users access to compute, storage and data access to EO/Geopspatial datasets, significantly simplifying the transition from traditional on-premise research to scalable, cloud-native processing.
They focus on providing computational resources located close to the data, minimizing data transfer and ensuring efficient execution of scientific workflows at scale. Platforms also integrate necessary APIs, connectors, and interfaces to ensure smooth interoperability with the EarthCODE Portal and other integrated services. They provide an offering through the Network of Resources and are already production ready services.
Their key responsibilities are:
- Provide scalable compute resources for big data Earth Observation (EO) analysis.
- Offering efficient data access to hosted EO/Geospatial datasets.
- Facilitate the execution of workflows developed on integrated FAIR Open Science Platforms.
- Supporting workflow execution close to data to minimize data transfer and enhance performance - to support the key EarthCODE paradigm of bringing code to the data.
- Integrating with EarthCODE's Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Register to the Network of Resources to ensure visibility and accessibility
- Providing documentation about the integration and usage of their platform
TIP
Providers may offer (and typically provide both) capabilities for infrastructure and FAIR Open Science together or separately.
EarthCODE Users
EarthCODE is designed for the community of Earth‑science practitioners, including ESRIN Science Hub members, the ESA Science Hub and teams working on ESA‑funded projects to enable them to do science and publish their results. It further serves as a place for developers and users to contribute workflows, platforms and discover openly available Earth Science research data and code. There are two key type of roles within EarthCODE:
Scientists, EarthCODE is a platform to: Do science. Publish science. Discover data and code. Use other people’s data and code in an ethical manner. Discuss science. Collaborate on science. Learn about FAIR and Open Science. Developers, EarthCODE is a space to: Expand the open-source ecosystem. Contribute tools and workflows. Develop reusable components and workflows, and discover and re-use the existing ones in an ethical way. Build FAIR-by-design services for the Earth science community.
For a detailed breakdown of roles and use cases, please refer to the Getting started with EarthCODE Page - Who is EarthCODE For?
At a high-level, these users are interested in and provided with the following capabilties from EarthCODE's ecosystem: 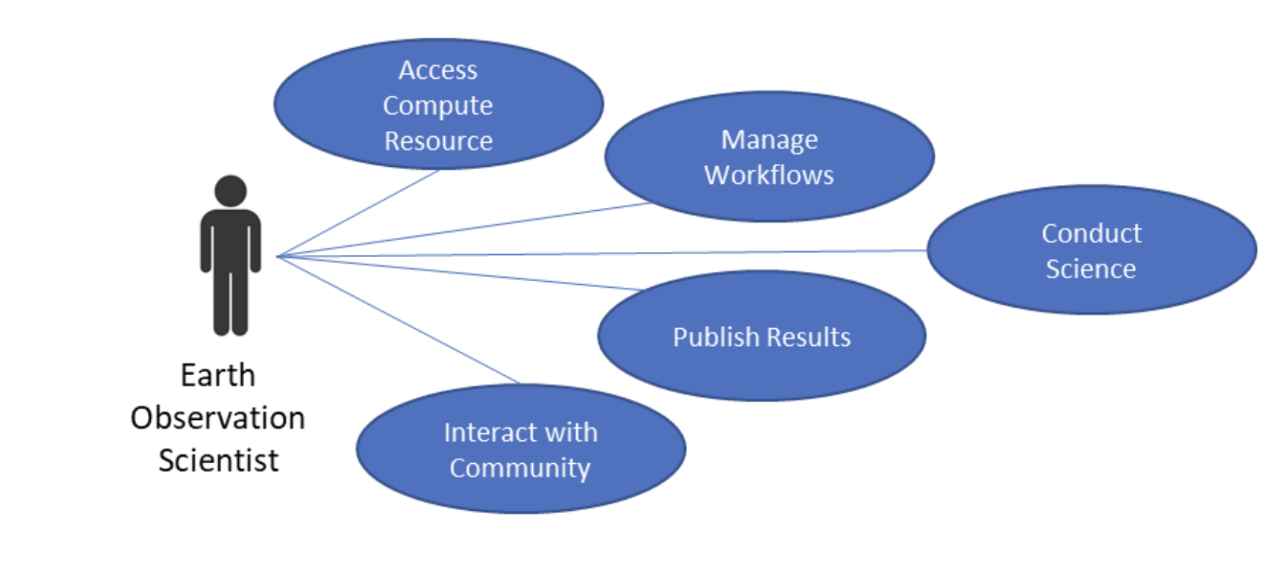
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Compute Resources | Request platform resources or access platform-integrated compute to run experiments - via the Network of Resources. Future updates may allow multi-platform access via a shared credit model. |
| Manage Workflows | Develop, configure, and version workflows on FAIR Open Science Platforms. These workflows can then be executed on infrastructure platforms. |
| Conduct Science | Execute the develop workflows to train models/analyze EO data directly on integrated platforms using familiar tools like Jupyter close to the data for scalability. Visualize datasets to explore and analyse. |
| Publish Results | Publish data products, experiments, and workflows in the Open Science Catalog using FAIR-compliant metadata through platform automation. |
| Interact with the Community | Share results with the community and enable them to easily analyse and visualize the results. Collaborate with peers, ask questions, and exchange ideas via forums, socials and events. |
Regarding examples of functionalities that EarthCODE platforms might provide, please refer to the 10 minutes to EarthCODE Page - Choosing a Platform.
Maintenance and Support
WIP
Content is being actively developed and updated for this page. EarthCODE's documentation is a living document and will be continuously updated with detailed reviews.