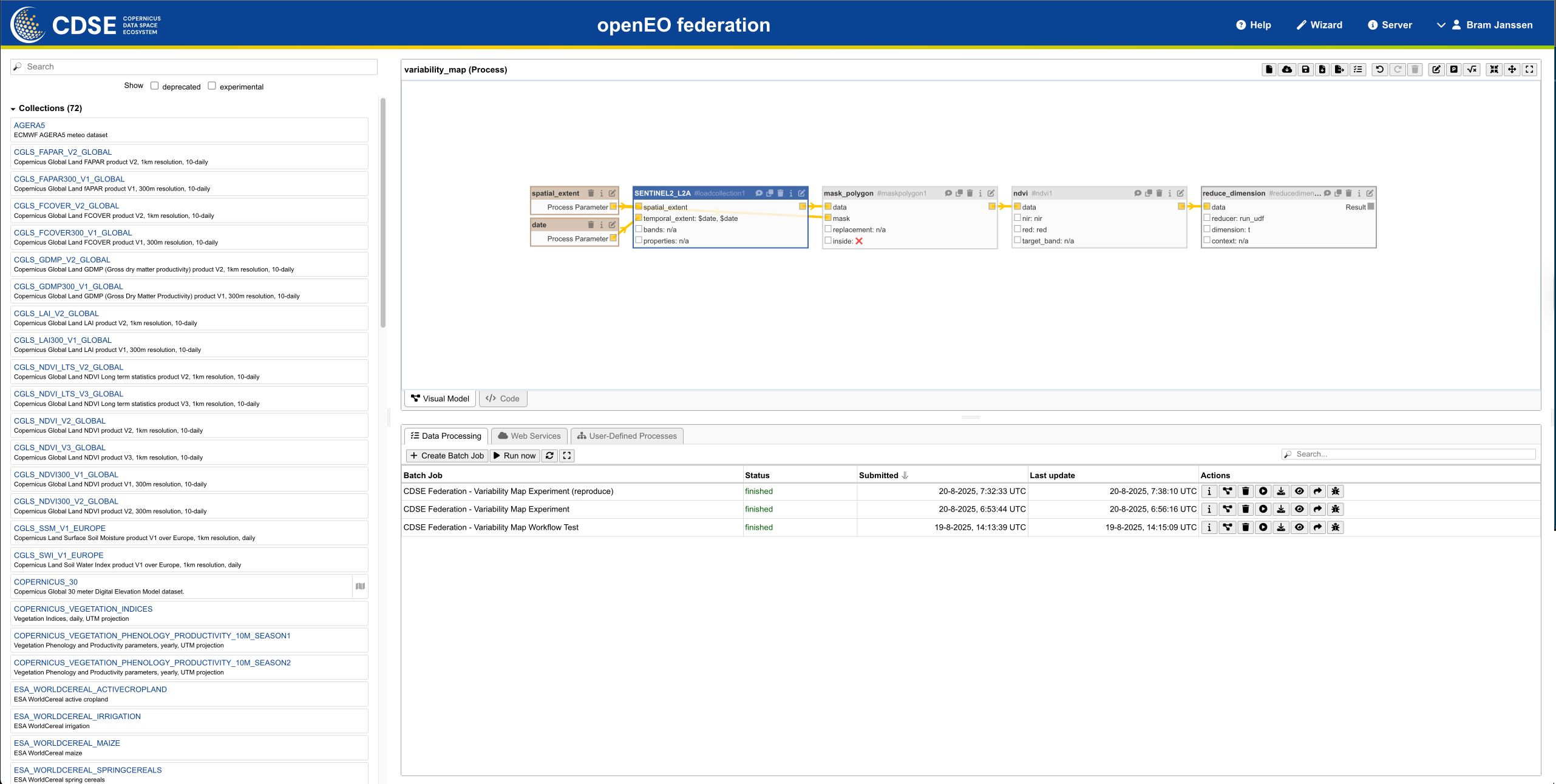
The Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem (CDSE) openEO federation provides a unified, cloud-based interface using the openEO API to access and process Earth observation data at scale. It enables scientists, analysts, and developers to run reproducible, standards-based workflows.
- Unified access to multiple openEO processing backends through a single, unified openEO API.
- Supports diverse domains by providing access to a wide range of Earth observation data sources, including the possibility to process your own data.
- Enables scalable workflows including datacube analytics, ML/AI inference, and EO product generation.
- Supports the development of interoperable workflows thanks to the openEO standard.