Reproducing an openEO Experiment published to the EarthCODE Open Science Catalogue
In this guide, we will use your newly published experiment from previous tutorial and reproduce it. This process will demonstrate how to leverage the openEO federation and EarthCODE tools to reproduce experiments, ensuring transparency and reproducibility in scientific research, reinforcing the principles of Open Science.
experiment_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ESA-EarthCODE/open-science-catalog-metadata-testing/c9ad31fd63330818e7895faf10f5104d9a101c01/experiments/cdse_federation_-_variability_map_experiment/process_graph.json"import rasterio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualise_tif(path: str):
with rasterio.open(path) as src:
data = src.read(1) # Read the first band
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(data, cmap='viridis')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()Connection with CDSE openEO Federation¶
The first step, before executing our published experiment in openEO, is to authenticate with an available openEO backend. In this example, we will use the CDSE openEO federation, which provides seamless access to both datasets and processing resources across multiple federated openEO backends.
import openeoconnection = openeo.connect(url="openeofed.dataspace.copernicus.eu").authenticate_oidc()Authenticated using refresh token.
Using the openEO client¶
The first option to execute an existing experiment is through the openEO Python client. By using openEO’s datacube_from_json, you can import the published experiment from the OSC into openEO.
experiment = connection.datacube_from_json(experiment_url)from IPython.display import JSON
JSON(experiment.to_json())path = "./files/varmap_experiment_reproduce.tiff"
experiment.execute_batch(
path,
title="CDSE Federation - Variability Map Experiment (reproduce)"
)visualise_tif(path)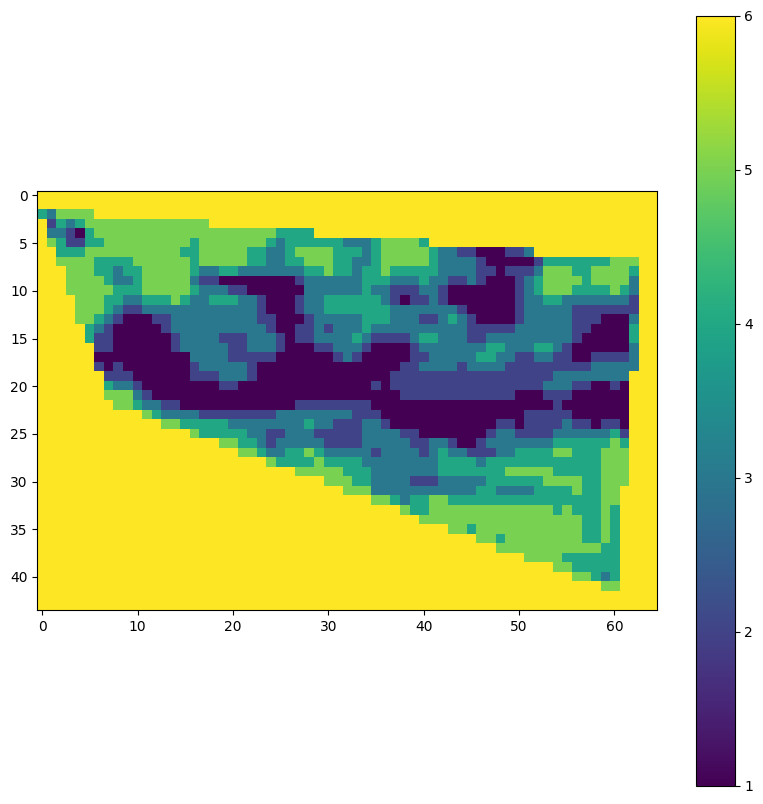
In this next step we will verify if the output products of the original experiment, created in the previous tutorial are the same as the output products of the reproduced experiment. This is done by comparing the output products of the original experiment with the output products of the reproduced experiment.
import numpy as np
def compare_geotiff(file1: str, file2: str) -> bool:
with rasterio.open(file1) as src1, rasterio.open(file2) as src2:
# Check if dimensions match
if src1.width != src2.width or src1.height != src2.height:
return False
# Check if coordinate reference systems match
if src1.crs != src2.crs:
return False
# Check if transform properties match
if src1.transform != src2.transform:
return False
# Compare pixel values
data1 = src1.read()
data2 = src2.read()
if not np.array_equal(data1, data2):
return False
return True
# Call the function with the specified files
are_equal = compare_geotiff("./files/varmap_experiment.tiff", "./files/varmap_experiment_reproduce.tiff")
print(f"Are the GeoTIFF files equal? {are_equal}")Are the GeoTIFF files equal? True
Using the openEO Web Editor¶
Using the experiment URL¶
Alternatively, you can also open the experiment through the openEO Web Editor using the experiment URL. This can be done by clicking the Import process from an external source button located in the top navigation bar.
Next, you can past the experiment URL into the window to fetch the experiment and open it in the editor.
Finally, click the Create Batch Job button to initiate the execution of the experiment.

Using the execution link from the published experiment¶
Whenever an experiment or workflow is published to the EarthCODE Open Science Catalogue, an execution link is generated. This link can be used to execute the experiment or workflow directly in the openEO Web Editor. As the integration of this execution link in the EarthCODE OSC is still in development, for now you can access the execution link through the GitHub repository of the EarthCODE Open Science Catalogue. The execution link is available in the links field of the experiment metadata. For example: https://

Navigating to this link will open the experiment in the openEO Web Editor, allowing you to execute it directly.